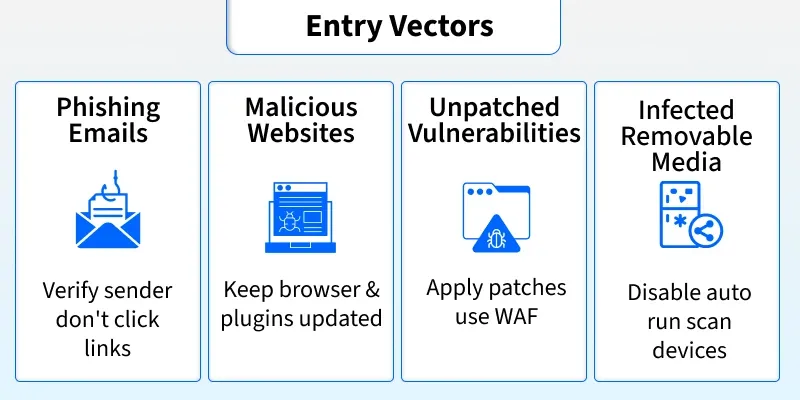
Malware is software that infects systems without user consent to steal sensitive data (bank details, passwords, personal emails), disrupt operations, or alter core system behavior. It can exfiltrate confidential information, corrupt or delete files, and impair system availability or integrity. Examples include ransomware (encrypts files for ransom) and spyware (monitors activity). Malware commonly spreads through phishing emails, malicious websites, unpatched vulnerabilities, and infected removable media.
Types of Malware
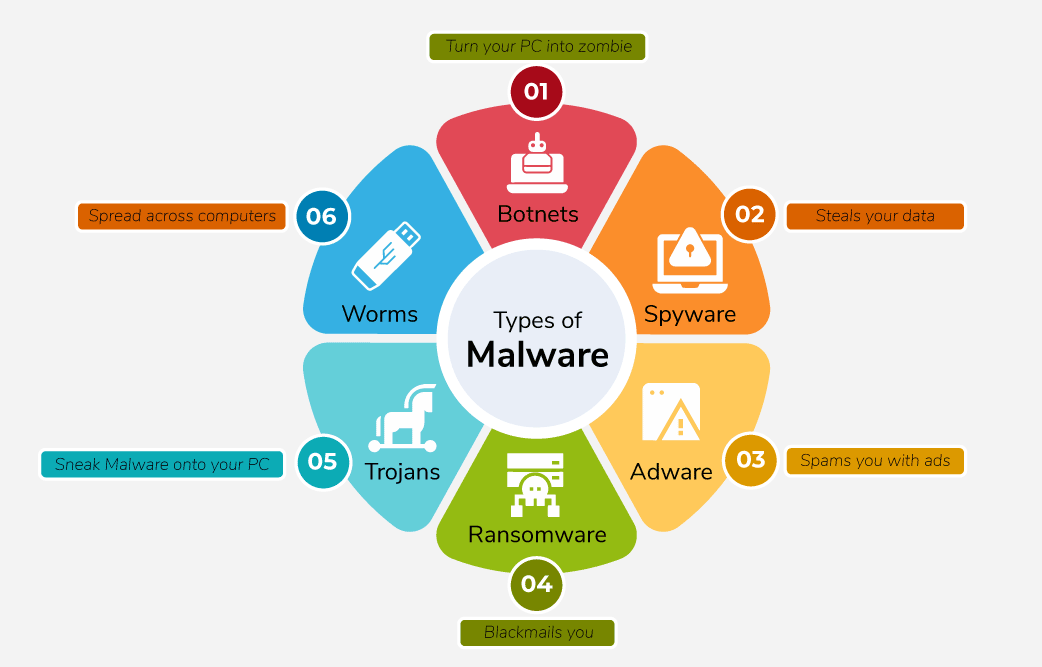
- Viruses: Malicious code attached to executable files. Spreads when files are shared; can delete or modify data.
- Worms: Self-replicating malware spreading across networks, slowing them down. Unlike viruses, they don’t need a host program.
- Trojan Horse: Appears legitimate (games, apps, files) but executes harmful operations in the background.
- Ransomware: Encrypts data and demands ransom for decryption.
- Adware: Displays unwanted ads/pop-ups, often bundled with software.
- Spyware: Monitors user activity and steals sensitive data.
- Logic Bombs: Malicious code triggered by specific events (e.g., a date or action).
- Rootkits: Modify the OS to create hidden backdoors for attackers.
- Backdoors: Secret entry points bypassing authentication to allow future access.
- Keyloggers: Record keystrokes to capture passwords and other credentials.
Signs Your Device Is Infected
- Slow performance and frequent crashes.
- Unexpected browser redirects to unknown sites.
- Fake infection warnings prompting paid fixes.
- Problems starting up or shutting down your computer.
- Persistent unwanted pop-up ads.
Why Do Cybercriminals Use Malware?
- Steal personal information for identity theft.
- Obtain credit card or financial data.
- Take control of multiple systems to launch DDoS attacks.
- Hijack systems to mine cryptocurrencies.
How To Protect From Malware
- Keep your operating system and software up to date.
- Install and regularly update trusted antivirus/antimalware tools.
- Never click suspicious links or pop-ups.
- Download apps only from trusted sources.
- Be cautious when opening email attachments or unknown links.
- Use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication.
How To Remove Malware
- Install a security tool such as Malwarebytes.
- Update malware definitions.
- Run a full system scan.
- Quarantine detected threats to isolate them.
- Remove or clean quarantined files.
- Reboot if prompted.
- Re-scan to confirm system health.
Tools Used to Remove Malware
- Malwarebytes
- SUPERAntiSpyware
- Microsoft Malicious Software Removal Tool (MSRT)
- Bitdefender Antivirus Free Edition
- Adaware Antivirus Free
- Avast Free Mac Security